What are Medicare Part B Excess Charges?
Medicare Part B excess charges refer to the additional costs that beneficiaries may face when they receive medical services from healthcare providers who do not accept Medicare assignment. Medicare assignment is an agreement between Medicare and healthcare providers, stating that the provider agrees to accept Medicare’s approved amount as full payment for services. However, some providers do not accept this assignment and may charge more than the Medicare-approved amount for their services. These additional charges are known as excess charges.
How Excess Charges Work
When a healthcare provider does not accept Medicare assignment, they can charge up to 15% above the Medicare-approved amount for their services. This additional amount is the excess charge, and it is the responsibility of the Medicare beneficiary to pay.
For example, suppose a Medicare beneficiary receives a covered service that has a Medicare-approved amount of $100. If the healthcare provider does not accept Medicare assignment, they can charge up to $115 for the same service, with the beneficiary responsible for paying the $15 excess charge out of pocket.
Understanding the Limiting Charge
While healthcare providers who do not accept Medicare assignment can charge up to 15% above the Medicare-approved amount, there are limits to how much they can charge. The limiting charge is the maximum amount that non-participating providers can charge for a covered service. It is set at 115% of the Medicare-approved amount.
Continuing with the previous example, if the Medicare-approved amount for a service is $100, the limiting charge would be $115. Therefore, even if the healthcare provider charges more than $115, the beneficiary is only responsible for paying the limiting charge of $115 plus any applicable deductible and coinsurance.
Who May Face Part B Excess Charges?
Medicare beneficiaries who receive services from healthcare providers that do not accept Medicare assignment may face excess charges. This situation commonly occurs with certain specialists, such as some physicians, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals.
It’s important to note that most healthcare providers accept Medicare assignment and do not charge excess fees. However, beneficiaries should always confirm whether a provider accepts Medicare assignment before receiving services to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket costs.
What states don’t allow Part B Excess Charges?
| State | CT | MA | MN | NY | OH | PA | RI | VT | All others |
| Part B Excess? | No | No | No | 5% cap | No | No | No | No | Yes |
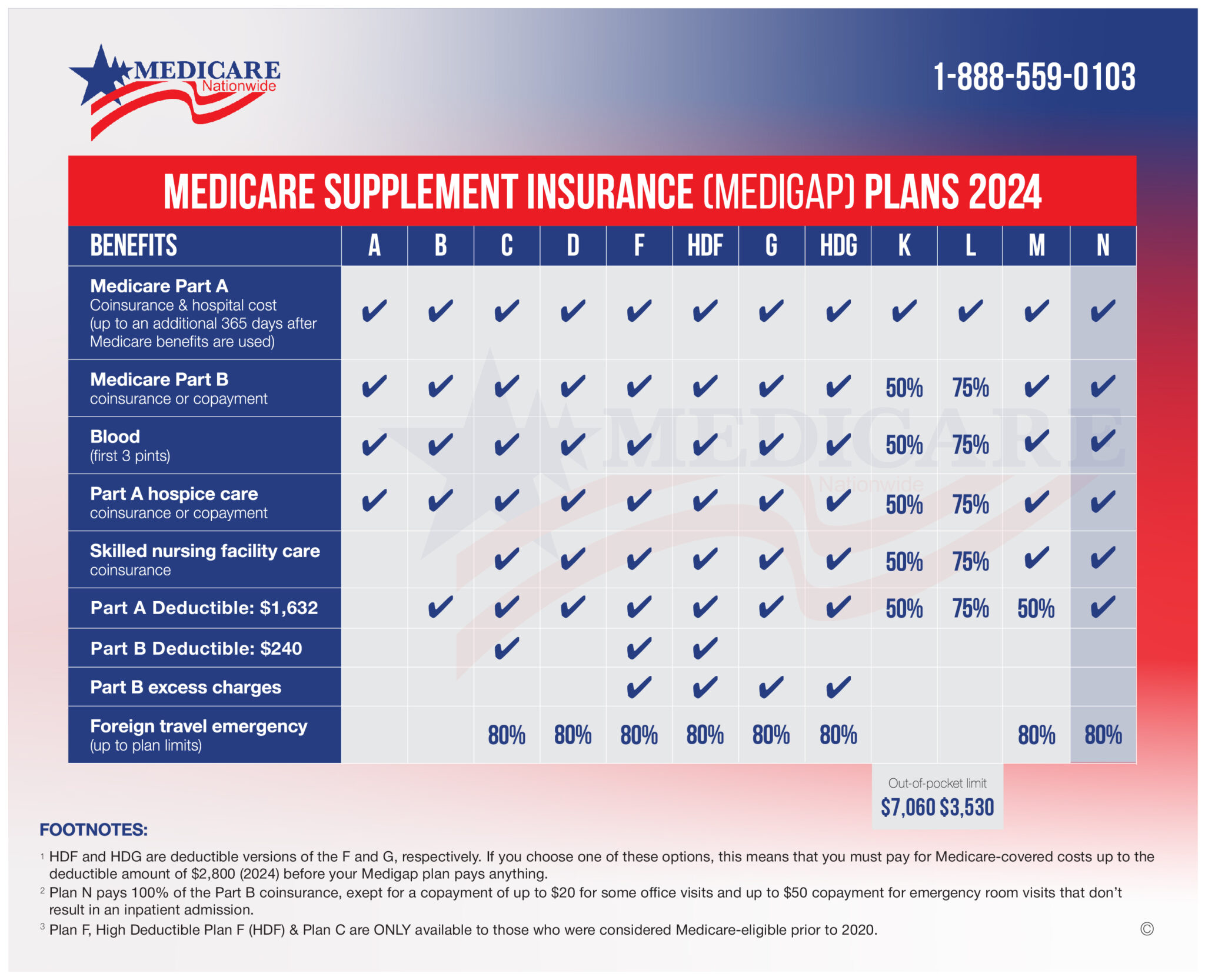
Does Medicare Supplement Plan N cover Part B Excess Charges?
Medicare Supplement Plan N does not typically cover Medicare Part B excess charges. While Medicare Supplement plans, also known as Medigap plans, provide additional coverage to help pay for out-of-pocket costs not covered by Original Medicare (Part A and Part B), coverage for Part B excess charges varies depending on the specific plan.
Medicare Supplement Plan N offers coverage for several Medicare cost-sharing expenses, including:
- Medicare Part A coinsurance and hospital costs up to an additional 365 days after Medicare benefits are exhausted.
- Medicare Part B coinsurance or copayment, except for a copayment of up to $20 for some office visits and up to a $50 copayment for emergency room visits that do not result in inpatient admission.
- First three pints of blood used in a medical procedure (annual limit).
- Hospice care coinsurance or copayment under Medicare Part A.
- Skilled nursing facility care coinsurance.
- Foreign travel emergency (up to the plan’s limits).
However, Medigap Plan N does not provide coverage for Medicare Part B excess charges. If you are enrolled in Plan N and receive services from healthcare providers who do not accept Medicare assignment, you may be responsible for paying any excess charges out of pocket.
If coverage for Part B excess charges is a concern for you, you may want to consider enrolling in a Medicare Supplement Plan that offers this coverage. Plans such as Plan F and Plan G typically cover Part B excess charges, providing beneficiaries with greater financial protection against these additional costs.
Before choosing a Medicare Supplement plan, it’s essential to carefully review the coverage options available in your area and consider your healthcare needs and budget. You can compare plan benefits and premiums using resources provided by Medicare or consult with a licensed insurance agent specializing in Medicare to find the best coverage option for you.
Impact on Medicare Beneficiaries
Excess charges can result in higher out-of-pocket costs for Medicare beneficiaries. These additional expenses can be particularly burdensome for individuals on fixed incomes or those with limited financial resources.
Moreover, excess charges can vary depending on the healthcare provider and the services rendered, making it challenging for beneficiaries to predict and budget for these costs accurately. As a result, beneficiaries may face financial strain or may even forgo necessary medical care due to concerns about affordability.
How to Avoid Part B Excess Charges
There are several strategies that Medicare beneficiaries can employ to avoid excess charges:
Choose Participating Providers: Whenever possible, choose healthcare providers who accept Medicare assignment. These providers agree to accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment for services, eliminating the risk of excess charges.
Verify Medicare Participation: Before receiving medical services, confirm with the healthcare provider whether they accept Medicare assignment. This information can usually be obtained by contacting the provider’s office directly or through Medicare’s online provider directory.
Consider Medigap Coverage: Medigap plans, also known as Medicare Supplement Insurance, can help cover some or all of the out-of-pocket costs associated with excess charges. Beneficiaries enrolled in Medigap plans that offer coverage for excess charges may have greater financial protection.
Explore Medicare Advantage Plans: Some Medicare Advantage plans offer coverage for excess charges, providing an alternative option for beneficiaries seeking protection against these additional costs.
Conclusion
Medicare Part B excess charges can present significant financial challenges for beneficiaries, potentially leading to higher out-of-pocket costs for medical services. Understanding how excess charges work and taking proactive steps to avoid them can help beneficiaries minimize their financial exposure and ensure access to affordable healthcare. By choosing participating providers, verifying Medicare participation, and exploring supplemental coverage options, beneficiaries can navigate the complexities of Medicare Part B with greater confidence and financial security.
Sources:
- Medicare.gov – “Assignment”: https://www.medicare.gov/assignment
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services – “Medicare Costs at a Glance”: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-General-Information/MedicareGenInfo/Costs/Costs-at-a-Glance
- KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation) – “Medicare Advantage 2022 Spotlight: First Look”: https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/medicare-advantage-2022-spotlight-first-look/

